In today’s article we will explore a common question: Is the gearbox part of the transmission? Understanding the difference can help you make an informed decision when researching Falk surplus gear reducers and parts.
Gearbox vs. Transmission
First, let’s take a look at what defines a gearbox and a transmission. Simply put: the gearbox is part of the transmission and serves a key role in applying power to the application. Transmissions and gearboxes are used on a wide variety of machine applications, from motor vehicles, to bicycles, to agricultural and industrial applications.
When choosing the right gearbox type, go with a gearbox supplier that has experience serving a wide range of industries. NW Industrial Sales, LLC has over 75 years of experience helping industries, from pulp and paper to oil and gas.
What is a Gearbox?
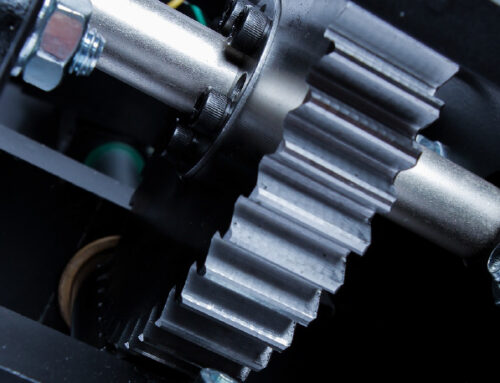
A gearbox is the primary part of the transmission that uses “gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque block conversions from a rotating power source to another device from a rotating power source to any other device.” They are used to change the speed, measured in rotations per minute, of a motor and allow an “output of torque and speed determined by the gear ratio.”
To use a gearbox bicycle as an example, the gears on the back wheel convert the torque and rotational speed from the cyclist pumping the pedals to match the gear needed to adjust ease of pedaling.
The phrase “5 speed transmission” is sometimes used to refer to the gearbox. To confuse things further, the terms “gearbox” and “gear reducer” can be used interchangeably.
Gearbox Types
- Helical Gearbox: Used for heavy-duty operations and low-power applications.
- Bevel Helical Gearbox: Typically used in mining applications and conveyors.
- Skew Bevel Helical Gearbox: Highly customizable, with a rigid structure.
- Worm Reduction Gearbox: Often used in applications relating to heavy industries, such as chemical and mineral.
- Planetary Gearbox: Used for robotics, 3D printing, and wherever high torque in a small space is required.
Gearboxes can also be configured for either automatic or manual transmissions.
What is a Transmission?
The transmission refers to the whole drivetrain, including the:
- Clutch
- Gearbox
- Differential
- Final drive shafts
The transmission often has multiple gear ratios and the ability to switch between them as changes in speed are needed. To use a car as an example, the gears can be either manual or automatically shifted. Transmissions can also provide directional changes, like forward or reverse.
How do Transmissions Work?
A transmission works by reducing the speed of the input shaft to create higher torque on the output shaft. This means that a small power source, or engine, can achieve higher torque than the output of the power source.
They can also manipulate the speed of the rotation by switching between different gear ratios, allowing for rapid adjustments based on the needs of the application. Gearboxes house the gears and are the main component of the transmission. Regular maintenance of the gearbox and gearbox parts ensures steady operation with minimal downtime.
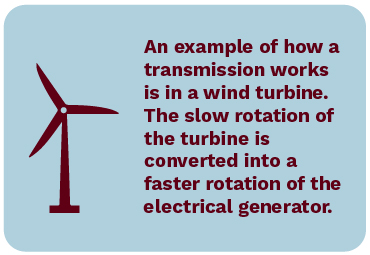
An example of how a transmission works is in a wind turbine. The slow rotation of the turbine is converted into a faster rotation of the electrical generator. While more complicated than some applications, the basic principle remains the same.
The Leading Falk Gearbox Supplier in Oregon
NW Industrial Sales, LLC offers a variety of Falk surplus gear reducers and parts backed by over 75 years of combined experience serving multiple industries. In addition to being a gearbox supplier, we offer a large inventory of Falk gearboxes and gearbox parts and are proud agents of Rexnord Industrial Services, granting you access to their nationwide maintenance network.
Whether you have questions about gearboxes or transmissions, or want to speak with one of our specialists, we are here to assist you 24/7.